IIT Hyderabad successfully tests 6G prototype on 7GHz band, paving way for ultra-fast internet rollout by 2030.India tests new G prototype at IIT Hyderabad, promising ultra-fast internet everywhere by 2030.
India’s Big Leap Towards 6G: IIT Hyderabad Successfully Tests Prototype, Rollout by 2030
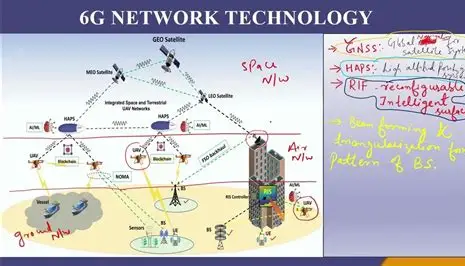
India is racing ahead in the global telecom revolution with a groundbreaking achievement in 6G technology. While many nations are still expanding their 5G networks, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Hyderabad has successfully tested a 6G prototype on the 7 GHz band, marking a strong milestone in the country’s digital journey. With this, India is positioning itself as a key player in shaping the future of ultra-fast internet connectivity.
Read This:
Airtel Festive Offer 2025: Free Google Storage, Apple Music & OTT for Prepaid Users
🚨India has set a target to roll out 6G by 2030, in line with the International Telecommunication Union’s IMT-2030 framework. pic.twitter.com/59oKxRyQgy
— Indian Infra Report (@Indianinfoguide) August 22, 2025
6G: A Giant Leap Beyond 5G
According to telecom researchers, every decade brings a new generation of mobile technology. Between 2010 and 2020, the world witnessed the development of 5G, which is still in the process of expanding across many regions. However, India has already shifted gears to prepare for 6G technology, expected to be rolled out globally by 2030.
Unlike 5G, which primarily focuses on high-speed mobile internet and IoT, 6 promises to take connectivity to new heights. Users will not only experience internet speeds several times faster but also enjoy seamless connectivity across cities, rural villages, oceans, skies, and even remote terrains.
IIT Hyderabad’s Breakthrough Test
The successful testing of the 6G prototype at 7 GHz was carried out with the support of multiple government bodies and telecom departments. Professor Kiran Kuchi, a leading telecommunications researcher at IIT Hyderabad, emphasized that India’s goal is not just to participate in the 6 races but to become a global leader.
She highlighted that the development journey began in 2021, and by 2030, when most countries start adopting this 6 techno, India will be ready with its own technology, ecosystem, and products. This aligns with the country’s broader “Viksit Bharat 2047” vision, which aims to make India a developed nation by 2047.
Read This:
Google AI Mode Update: Exciting Hindi Among 5 New Languages
Features and Benefits of 6G
The introduction of 6 will bring transformational changes to how we connect, communicate, and consume digital services. Some of the key benefits include:
- Ultra-Fast Speeds – Internet speed expected to be 100x faster than 5G.
- Universal Connectivity – From villages to cities, from land to sky, uninterrupted access will be possible.
- Low Power Systems – IIT Hyderabad has already designed low-power chips to make devices more efficient.
- AI-Powered Performance – Development of 6G AI High-Performance Chips will enhance automation, smart cities, and Industry 4.0 applications.
- Global Leadership – India aims to not just adopt but shape the new G ecosystem.
6G’s Role in India’s Digital Future
Currently, India is rapidly rolling out 5G networks across urban and rural areas, but the government is also investing heavily in the next generation of telecom technologies. The success of IIT Hyderabad’s project demonstrates India’s readiness to leap ahead.
The adoption of 6 will play a critical role in sectors such as:
- Healthcare: Real-time remote surgeries with zero lag.
- Education: Immersive learning using VR/AR classrooms.
- Agriculture: Smart farming with IoT-based precision tools.
- Transportation: Seamless support for autonomous vehicles and drones.
- Defence & Aerospace: High-speed communication for advanced security systems.
India as a Global 6G Innovator
With this achievement, India joins a select group of countries working on next-generation telecom networks. Nations like the USA, South Korea, Japan, and China are also exploring 6 technologies. However, India’s focus on developing homegrown solutions and low-cost ecosystems gives it an edge in catering to both domestic and international markets.
Professor Kiran Kuchi stressed that India’s involvement will ensure that the country is not dependent on global giants but can emerge as a technology exporter in the 6G era.

4G vs 5G vs 6G: A Quick Comparison
| Feature / Tech | 4G | 5G | 6 (Upcoming by 2030) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Launch Year | ~2010 | ~2020 | Expected ~2030 |
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 1 Tbps (theoretical) |
| Latency | 30–50 ms | 1–10 ms | <1 ms (near real-time) |
| Spectrum Band | 2–8 GHz | 24–100 GHz (mmWave) | Above 100 GHz, incl. Terahertz (THz) |
| Coverage | Cities & towns | Urban + Semi-rural | Universal (cities, villages, sea, sky, space) |
| Connectivity Density | ~2,000 devices/km² | ~1 million devices/km² | 10 million+ devices/km² |
| Key Use Cases | Mobile Internet, Video Streaming, Social Media | IoT, Smart Cities, AR/VR, Autonomous Vehicles | Metaverse, Holographic Calls, Smart Agriculture, Remote Surgeries, Space Communication |
| Power Efficiency | Moderate | High | Ultra High (low-power chips) |
| AI Integration | Minimal | Limited | Core to System (6G AI Chips) |
Read Ahead
The global rollout of 6 is expected around 2030, and by then, India aims to have an established 6G ecosystem. With IIT Hyderabad leading research, and strong government backing, India is well-positioned to redefine the global telecom landscape.
As the world looks forward to the next generation of connectivity, India’s bold step ensures that the nation will play a central role in shaping the digital future.

